Chicken pox in pregnancy (Varicella Zoster Virus)
Gynaecology
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding : Management in Primary Care
Chicken Pox In Pregnancy (Varicella Zoster Virus)
Dr ‘FUNMI ODUSOGA DFSRH MRCOG
Table of content
1. Incidence
2. Presentation
3. Investigations
4. Management
5. Prevention
6. Reference
- Incidence
- Presentation
- Investigations
- Management
- Prevention
Incidence
- Primary VZV infection in pregnancy is uncommon ( 3 in 1000 pregnancies)
- Incubation period 1-3weeks
- 80% of patients tested will have VZV IgG (immune)
- Women from tropical and subtropical are more susceptible because they are more likely to be seronegative for VZV IgG
- Risk from immunocompetent individual in non-exposed area e.g. thoracolumbar area is remote but can occur
- Risk from Disseminated zoster or exposed zoster e.g. ophthalmic or immunocompromised patient is high-(Viral shedding is greater)
- No increase in risk of miscarriage in 1st trimester
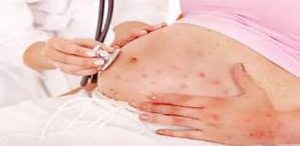
History And Presentation
- Pregnant woman present with history of contact with chicken pox or a rash
- Period of infectivity is 1 day before eruption of rash until lesion have crusted over
- Ask about type of VZV infection they were exposed to
- Timing of exposure
- Closeness & duration of contact (Significant if > 15 minutes, face to face contact or large open ward)
- Symptoms of severe chicken pox are:
- Respiratory symptoms e.g Pneumonia
- Neurological symptoms e.g. photophobia, seizure or drowsiness
- Haemorrhagic rash or bleeding
Maternal Risk
- Increased morbidity in adults
- Pneumonia 10-14% (More severe at later gestational age)
- Hepatitis
- Encephalitis
- Rarely death 0-14%
Fetal Risk
- Risk of spontaneous miscarriage not increased in 1st trimester
- Small risk of fetal varicella syndrome exist if in the 1st 28 weeks of pregnancy approx. 1%
Features of Fetal Varicella syndrome are
- Skin scarring in dermatomal distribution
- Eye defects (microphthalmia, chorioretinitis or cataract)
- hypoplasia of the limbs
- Neurological microcephaly, cortical atrophy, mental retardation, bowel and bladder sphincter dysfunction)
Investigations
- Do blood test to check immunity i.e. VZV IgG in pregnant woman in contact with chicken pox with no previous history or uncertain history of chicken pox
- (Administer Varicella zoster immunoglobulin if not immune)
- Refer for fetal medicine specialist scan at 16-20weeks or 5weeks after infection
- Amniocentesis has strong negative predictive value but poor positive predictive value in detecting fetal damage
- Fetal MRI (Provides additional information if there is morphological abnormalities
Management
- Refer all women with chicken pox to medical department and avoid maternity wards to prevent spread to other pregnant women and neonates
- Administer VZ Immunoglobulin as soon as possible if non immune patients are exposed to chicken pox. It is effective when given up to 10 days after contact
- Administer 2nd dose if further exposure and 3 weeks have elapsed
- Patient with hypogammaglobinaemia who are already receiving replacement therapy with immunoglobulin do not require VZIG (Increased risk of anaphylaxis)
- Manage non immune pregnant women as being potentially infectious 8-28 days after they receive VZIG and 8-21 days after exposure if they do not receive VZIG
- Isolate pregnant women who develop chicken pox rash from other pregnant women
- Prescribe Oral acyclovir 800mg 5 times daily for 7 days if they present within 24 hours of onset of rash
- Manage other clinical features symptomatically e.g antipyrexial, anti-pruritic medication
- Give intravenous acyclovir in all pregnant women with severe chicken pox
- Refer all patients with severe Chicken pox to hospital immediately (avoid maternity department)
- Nurse hospitalised patients in isolation from babies , pregnant women and non-immune staff
Prevention
- Offer Varicella vaccine pre-pregnancy or post-partum
- Advice non-immune pregnant women to avoid contact with chicken pox and shingles during pregnancy
- Non pregnant women who are vaccinated should avoid getting pregnant for 4weeks after completing the 2 dose of vaccination schedule
- Women with chicken pox should avoid contact with other pregnant women and neonates until the rashes have crusted over
- Non immune pregnant women who have been exposed to chicken pox are potentially infectious from 8-28days if they receive VZIG and 8-21days if they do not
